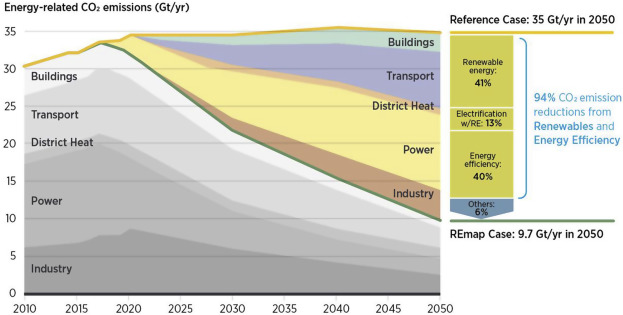
In recent years, the world has witnessed a remarkable transformation in energy markets, driven primarily by the rapid growth of renewable energy sources. This shift is not just a response to climate change but also a result of technological advancements, economic considerations, and changing consumer preferences. As nations strive to reduce their carbon footprints and meet international climate commitments, renewable energy has emerged as a pivotal player in reshaping the global energy landscape.
The Changing Energy Paradigm
Historically, energy production was dominated by fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas. However, the environmental implications of fossil fuel consumption have become increasingly apparent. From air pollution to greenhouse gas emissions, the urgent need for sustainable alternatives has never been clearer. In response, countries around the world are investing heavily in renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewables are expected to account for nearly 95% of the increase in global power capacity through 2026. This significant shift not only reflects the growing viability of renewable energy but also highlights the declining costs associated with these technologies. The cost of solar photovoltaics, for instance, has decreased by around 90% over the past decade, making it one of the most economically attractive sources of energy available.
Technological Advancements Driving Change
Innovation has been a critical factor in the rise of renewable energy. Advances in energy storage, grid integration, and smart technology have made it possible to harness and distribute renewable energy more efficiently. Battery technology, particularly, has seen rapid improvements, allowing for better storage of energy produced during peak generation times.
Moreover, smart grid technologies enable a more flexible and reliable energy system. They facilitate the integration of diverse energy sources, manage demand more effectively, and improve the overall resilience of energy infrastructure. This evolution in technology is not only making renewable energy more accessible but also enhancing energy security and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Economic Impacts and Job Creation
The renewable energy sector has become a significant driver of economic growth and job creation. According to the IEA, the global renewable energy workforce reached 12 million in 2020, with this number expected to rise as investments in clean energy continue to grow. Jobs in solar and wind energy, in particular, have seen substantial increases, offering new opportunities for skilled labor in a rapidly changing job market.
Investment in renewable energy is not only about job creation but also about fostering economic resilience. By diversifying energy sources and reducing reliance on imported fuels, countries can enhance their energy independence and stabilize their economies against global market fluctuations.
Policy Support and International Cooperation
The shift towards renewable energy is significantly influenced by government policies and international agreements aimed at curbing climate change. The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, prompting countries to accelerate their transition to cleaner energy sources. Many nations have introduced incentives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks to encourage the adoption of renewables, fostering a more conducive environment for investment.
International cooperation is also critical in this energy transition. Organizations like the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) facilitate knowledge sharing and capacity building, enabling countries to learn from one another’s experiences. Collaborative efforts to develop technology and share best practices are vital for accelerating the global transition to renewable energy.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the positive momentum, the transition to renewable energy is not without its challenges. Issues such as regulatory hurdles, infrastructural constraints, and the need for substantial upfront investments remain significant obstacles. Additionally, the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind requires ongoing advancements in energy storage and grid management.
Furthermore, the geopolitical landscape is shifting as countries compete for leadership in the renewable energy sector. Nations that invest early and effectively in clean technologies stand to gain economically and politically in the new energy economy. This competition could lead to tensions but also presents opportunities for collaboration and innovation.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future
As we move towards a more sustainable future, the role of renewable energy will only continue to expand. The convergence of technological advancements, economic viability, and supportive policies is creating a fertile ground for a cleaner, more resilient energy landscape. The commitment to renewable energy not only addresses the pressing issue of climate change but also opens up pathways for economic growth and job creation.
The world stands at a pivotal juncture, where the choices made today will shape the energy systems of tomorrow. By embracing renewable energy, nations can build a sustainable future that benefits both the planet and its inhabitants, ensuring a cleaner, greener world for generations to come.